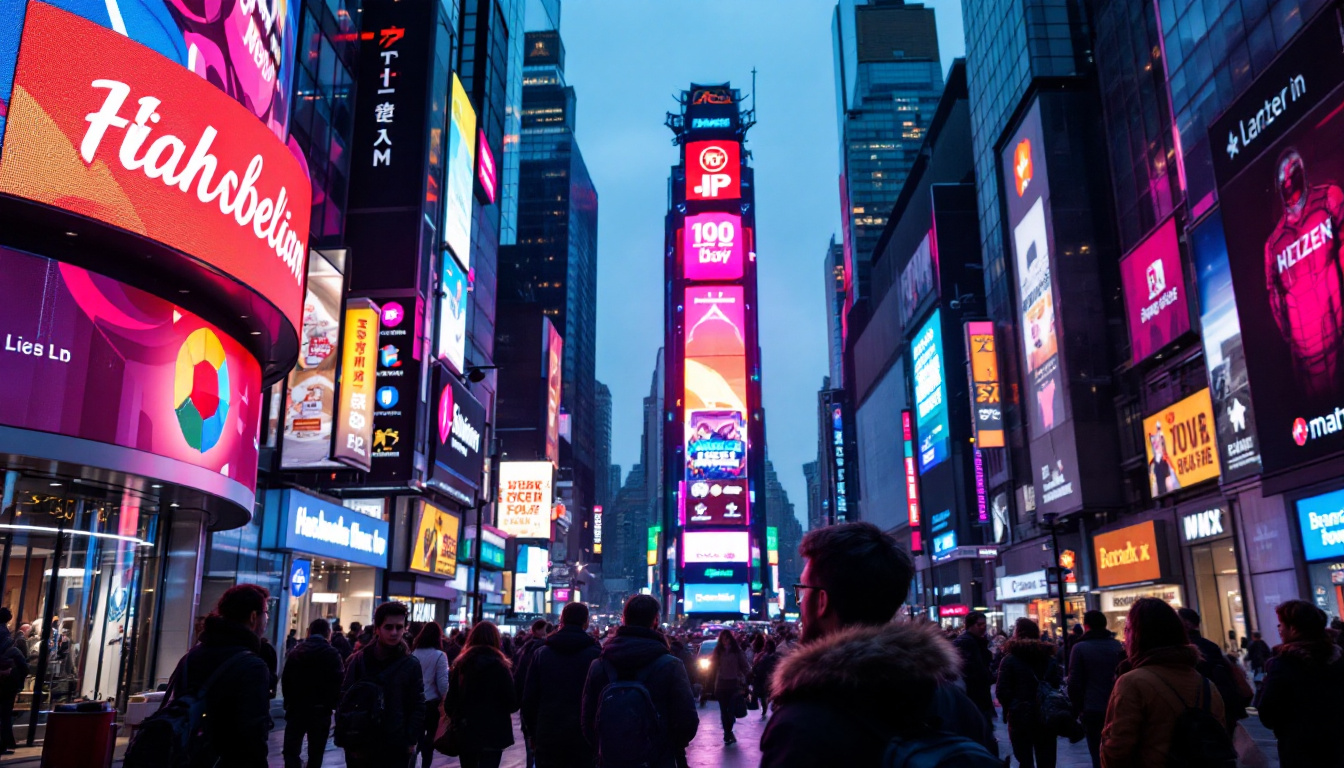
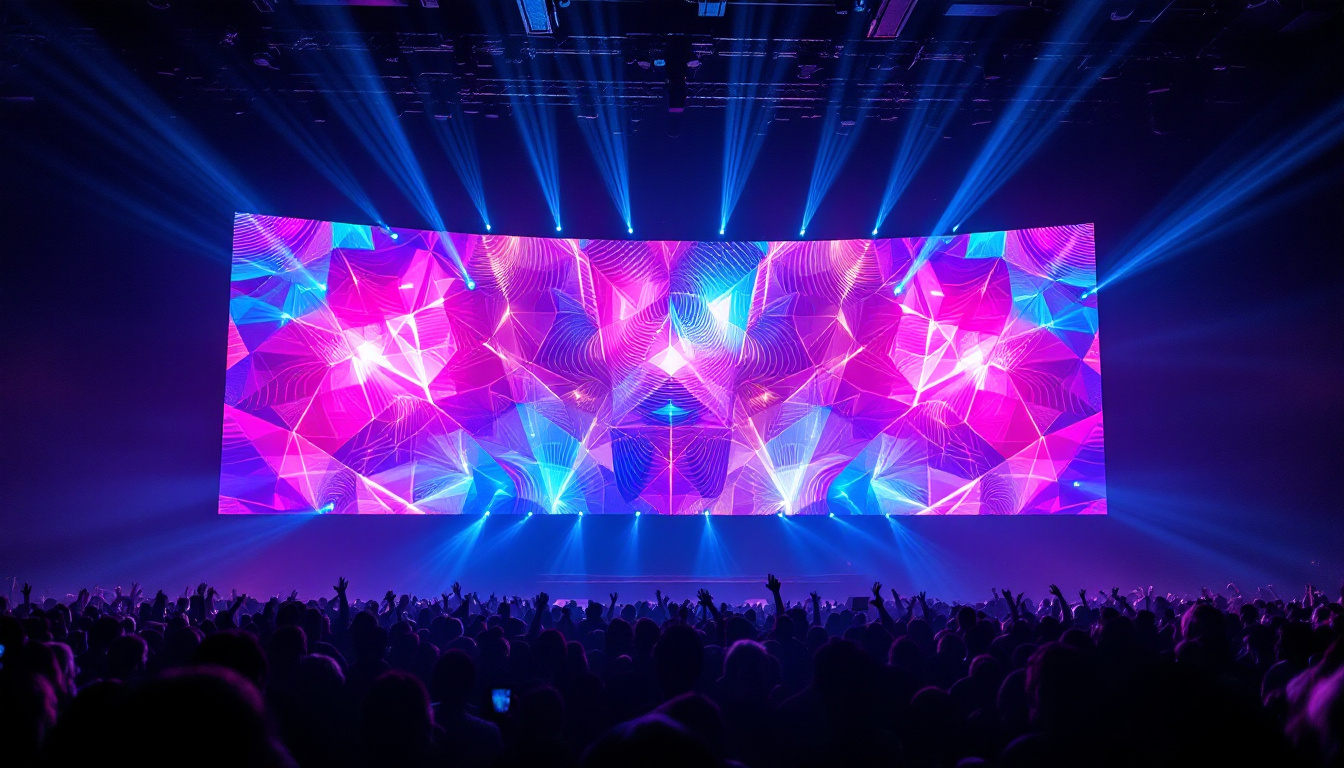
In recent years, LED technology has revolutionized the way we illuminate spaces and convey information through displays. Background LED lighting, in particular, has gained significant traction in various applications, from residential settings to commercial environments. This article delves into the intricacies of LED displays, their advantages, applications, and the technology behind them.
Understanding LED Technology
Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs) are semiconductor devices that emit light when an electric current passes through them. This technology has evolved dramatically since its inception, leading to a wide range of applications, particularly in the realm of lighting and displays. Originally developed in the early 1960s, LEDs were limited to low-intensity red light applications. However, advancements in materials and manufacturing processes have paved the way for the vibrant, multi-colored LEDs we see today, which are used in everything from home lighting to large-scale commercial displays.
The Basics of LED Functionality
At the core of LED functionality is the principle of electroluminescence. When electrons recombine with holes in the semiconductor material, energy is released in the form of photons, producing light. This process is highly efficient compared to traditional incandescent and fluorescent lighting, making LEDs a preferred choice for many applications. The efficiency of LEDs not only translates to lower energy consumption but also means that they generate less heat, which can be a significant advantage in various settings, reducing the need for additional cooling systems.
LEDs are available in various colors, which are determined by the materials used in their construction. The ability to produce a wide spectrum of colors allows for creative and dynamic lighting solutions that can enhance any environment. For instance, RGB (red, green, blue) LEDs can be combined in different intensities to create millions of colors, enabling applications in mood lighting, stage productions, and even architectural designs that change color and intensity based on the time of day or specific events.
Advantages of LED Displays
LED displays offer numerous advantages over traditional display technologies. One of the most significant benefits is their energy efficiency. LEDs consume significantly less power, which not only reduces electricity bills but also contributes to environmental sustainability. This efficiency is particularly important in large-scale installations, such as outdoor billboards or stadium screens, where the cumulative energy savings can be substantial over time.
Additionally, LED displays provide superior brightness and contrast ratios, making them ideal for outdoor and high-ambient-light environments. Their durability and longevity further enhance their appeal, as they can last up to 100,000 hours, far exceeding the lifespan of conventional display technologies. This durability is complemented by their resistance to shock and vibration, making them suitable for a variety of applications, from public transportation systems to retail environments. Furthermore, the rapid response time of LEDs allows for high refresh rates, which is crucial for displaying fast-moving images without blurring, making them a favorite choice for video walls and digital signage in busy urban settings.
Applications of Background LED Lighting
Background LED lighting has found its way into a myriad of applications, each leveraging the unique properties of LEDs to create engaging and functional environments. From commercial spaces to residential settings, the versatility of LED technology is evident.
Commercial Uses
In commercial settings, LED displays are often used for advertising and branding. Retailers utilize vibrant LED screens to attract customers and showcase products. The ability to change graphics and messages quickly makes LED displays an effective marketing tool.
Moreover, LED lighting is widely used in hospitality venues, such as restaurants and hotels, to create ambiance and enhance the customer experience. Dynamic lighting can influence mood and perception, making it a crucial element in the design of these spaces. For instance, a restaurant may use warm LED tones to create an inviting atmosphere during dinner service, while brighter, cooler lights may be employed during brunch hours to energize the environment. This strategic use of lighting not only enhances the dining experience but can also increase customer dwell time, ultimately boosting sales.
Residential Applications
In residential environments, background LED lighting is increasingly popular for its aesthetic and functional benefits. Homeowners use LED strips and panels to create ambient lighting in living rooms, bedrooms, and kitchens. The versatility of LED lighting allows for customization, enabling individuals to set the mood for any occasion.
Additionally, LED technology is often integrated into smart home systems, allowing homeowners to control lighting remotely or automate it based on their preferences. This integration enhances convenience and energy efficiency, making LED lighting an attractive option for modern homes. For example, homeowners can program their LED lights to gradually brighten in the morning, simulating a natural sunrise, which can help improve wakefulness and overall mood. Furthermore, with the rise of voice-activated assistants, adjusting lighting has never been easier; a simple command can change the color and intensity of lights to match the homeowner’s desired atmosphere, whether it’s a cozy movie night or a vibrant gathering with friends.
The Technology Behind LED Displays
The technology that powers LED displays is intricate and multifaceted. Understanding the components and processes involved can provide insight into why these displays are so effective and popular.
Components of LED Displays
LED displays consist of several key components, including the LED modules, control systems, and power supplies. The LED modules contain the individual diodes that emit light, while the control systems manage the display’s operation, including the content being shown.
Power supplies are crucial for providing the necessary voltage and current to the LEDs. The efficiency of these components directly impacts the overall performance and longevity of the display. Additionally, thermal management systems are often integrated to dissipate heat generated by the LEDs during operation. This is vital, as excessive heat can lead to reduced performance and a shortened lifespan of the display. Advanced cooling solutions, such as heat sinks and fans, are commonly employed to ensure optimal operating temperatures, thus enhancing reliability and maintaining vibrant image quality over time.
Display Technologies
There are various types of LED display technologies, each with its own advantages and use cases. Among the most common are Direct View LED (DVLED) displays and LED-backlit LCD displays. DVLED displays utilize individual LEDs to create images directly, offering superior brightness and contrast.
On the other hand, LED-backlit LCD displays use LEDs to illuminate an LCD panel. While these displays are generally less bright than DVLEDs, they are often more cost-effective and can still deliver excellent image quality for many applications. Furthermore, advancements in LED technology have led to the development of OLED (Organic Light Emitting Diode) displays, which provide even deeper blacks and a wider color gamut. OLEDs function by using organic compounds that emit light when an electric current is applied, allowing for thinner and more flexible display designs. This has opened up new possibilities for innovative applications, such as curved screens and wearable technology, further expanding the horizons of display technology.
Design Considerations for LED Displays
When designing spaces that incorporate LED displays, several factors must be considered to maximize their effectiveness and aesthetic appeal. These considerations range from placement and size to color temperature and brightness.
Placement and Size
The placement of LED displays is crucial for ensuring visibility and engagement. Displays should be positioned at eye level and within a reasonable distance for optimal viewing. Size also plays a significant role; larger displays can be more impactful but may require more space and careful integration into the overall design.
In commercial settings, strategic placement can enhance customer interaction. For instance, placing displays near entrances or checkout areas can capture attention and drive sales.
Color Temperature and Brightness
Color temperature refers to the warmth or coolness of the light emitted by the LEDs. Choosing the right color temperature can influence the ambiance of a space. Warmer tones are often preferred in residential settings for a cozy feel, while cooler tones may be more suitable for commercial environments that require a more energetic atmosphere.
Brightness is another critical factor. Displays must be bright enough to be seen in various lighting conditions, especially in outdoor applications. Adjustable brightness settings can help maintain visibility while conserving energy.
Future Trends in LED Display Technology
The future of LED display technology is promising, with ongoing advancements that are set to enhance performance and expand applications. Innovations in materials, control systems, and integration with emerging technologies are paving the way for more dynamic and versatile displays.
Advancements in Materials
Research into new materials is leading to the development of more efficient and brighter LEDs. Organic LEDs (OLEDs), for instance, offer the potential for flexible displays that can be integrated into various surfaces, creating new design possibilities.
Additionally, advancements in quantum dot technology are improving color accuracy and brightness, making displays more vibrant and lifelike. These innovations are likely to drive the next generation of LED displays, pushing the boundaries of what is possible.
Integration with Smart Technologies
As smart technology continues to evolve, the integration of LED displays with IoT devices is becoming increasingly common. This integration allows for real-time data display, interactive experiences, and enhanced user engagement.
For example, in retail environments, LED displays can be connected to inventory systems to showcase real-time product availability. In smart homes, displays can be used to provide information on energy consumption, weather updates, and more, enhancing the overall user experience.
Conclusion
Background LED lighting and displays have transformed the way we illuminate and interact with our environments. Their energy efficiency, versatility, and aesthetic appeal make them a preferred choice across various applications. As technology continues to advance, the potential for LED displays will only grow, leading to even more innovative uses and designs.
Understanding the intricacies of LED technology, its applications, and future trends is essential for anyone looking to leverage this powerful tool. Whether in commercial or residential settings, the impact of LED displays is profound, creating engaging environments that enhance both functionality and experience.
Illuminate Your Space with LumenMatrix
Ready to elevate your environment with the cutting-edge LED display technology discussed in this article? LumenMatrix is at the forefront of creating immersive visual experiences with a diverse range of LED display solutions. From captivating Indoor LED Wall Displays to dynamic Outdoor LED Wall Displays, and innovative options like Vehicle LED Displays and LED Transparent Displays, we have everything you need to transform your space. Embrace the future of visual communication with LumenMatrix and make a lasting impression. Check out LumenMatrix LED Display Solutions today and see your vision come to life.