In the modern world, displays have become an integral part of our daily lives. From smartphones to televisions, the technology behind these screens plays a crucial role in how we interact with devices. Among the various types of displays, LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) and LED (Light Emitting Diode) technologies stand out for their clarity, efficiency, and versatility. This article delves into the intricacies of LCD screens, touch screens, and LED displays, providing a comprehensive understanding of each technology.
Understanding LCD Technology
LCD technology has revolutionized the way visual information is presented. It utilizes liquid crystals sandwiched between two layers of glass or plastic, which manipulate light to produce images. The fundamental principle behind LCDs is their ability to control the passage of light through the liquid crystals, which can be aligned in various ways to create colors and images.
The Components of LCD Screens
LCD screens consist of several key components that work together to deliver high-quality visuals. These include:
- Liquid Crystals: The core element responsible for image formation. These crystals change orientation when an electric current is applied, allowing light to pass through or be blocked.
- Backlight: Since liquid crystals do not emit light on their own, a backlight is essential. Typically, this is provided by fluorescent tubes or LEDs.
- Polarizers: These layers are crucial for controlling light. They ensure that only light waves aligned in a specific direction can pass through, enhancing contrast and color accuracy.
How LCD Screens Work
The operation of an LCD screen begins with the backlight illuminating the liquid crystals. When an electric current is applied, the orientation of the liquid crystals changes, allowing varying amounts of light to pass through. This manipulation of light creates the images seen on the screen. Color is produced by using a combination of red, green, and blue (RGB) filters, which blend together to form a full spectrum of colors.
One of the significant advantages of LCD technology is its energy efficiency. Compared to older technologies like cathode ray tubes (CRTs), LCDs consume less power and generate less heat, making them a preferred choice for a wide range of applications. This energy efficiency not only contributes to lower electricity bills but also aligns with the growing demand for environmentally friendly technology.
Moreover, LCD screens are known for their slim profile and lightweight design, which have made them the standard for modern televisions, computer monitors, and portable devices. The advancements in LCD technology have also led to the development of high-definition (HD) and ultra-high-definition (UHD) displays, providing users with sharper images and more vibrant colors. These improvements have transformed the viewing experience, making it more immersive and engaging, whether for gaming, watching movies, or professional graphic design.
Touch Screen Technology
Touch screens have transformed the way users interact with devices. By allowing direct interaction with what is displayed, they provide a more intuitive experience. Touch screen technology can be integrated with various display types, including LCDs, to enhance functionality.
Types of Touch Screen Technologies
There are several types of touch screen technologies, each with its unique advantages and applications:
- Resistive Touch Screens: These screens consist of two flexible layers separated by a small gap. When pressure is applied, the layers touch, completing an electrical circuit. They are cost-effective and work well with gloves or styluses but offer lower clarity and sensitivity compared to other types.
- Capacitive Touch Screens: These screens use the electrical properties of the human body. They are more sensitive and provide better clarity and multi-touch capabilities. However, they require direct contact with a finger and may not work with gloves.
- Infrared Touch Screens: Utilizing an array of infrared sensors, these screens detect touch by measuring interruptions in the infrared light beams. They offer high durability and can work with any object, but they may be more expensive to implement.
Applications of Touch Screens
Touch screens are widely used across various industries. In consumer electronics, smartphones and tablets rely heavily on touch technology for user interaction. In retail, touch screens facilitate self-service kiosks, allowing customers to browse and purchase products efficiently. Additionally, in healthcare, touch screens are used in medical devices and patient management systems to streamline operations.
The growing popularity of touch screens can be attributed to their ability to simplify user interfaces and enhance user engagement. As technology continues to advance, touch screens are expected to become even more prevalent in everyday devices.
Moreover, touch screens are making significant inroads in educational settings, where interactive whiteboards and tablets are revolutionizing the way students learn. These devices enable educators to create engaging, interactive lessons that can cater to various learning styles. The tactile feedback of touch screens allows students to interact directly with educational content, fostering a more hands-on approach to learning. This shift not only enhances comprehension but also encourages collaboration among students, as they can easily share their screens and work together on projects in real-time.
In the automotive industry, touch screen technology is also gaining traction, with many modern vehicles featuring touch-based infotainment systems. These systems allow drivers to control navigation, music, and communication features with simple gestures, minimizing distractions while driving. As manufacturers continue to innovate, we can expect to see even more sophisticated touch interfaces that integrate voice recognition and gesture control, creating a seamless and safer driving experience.
LED Display Technology
LED displays are often confused with LCDs, but they represent a different technology. While LCDs use liquid crystals and require a backlight, LED displays utilize light-emitting diodes to create images directly. This distinction leads to several advantages in terms of brightness, contrast, and energy efficiency.
How LED Displays Work
LED displays consist of tiny light-emitting diodes that emit light when an electric current passes through them. These diodes can produce a wide range of colors by adjusting the intensity of the red, green, and blue components. Unlike traditional LCDs, which rely on a backlight, LED displays can achieve deeper blacks and higher contrast ratios since individual pixels can be turned off completely.
This capability allows for more vibrant colors and improved image quality, making LED displays particularly popular for high-definition televisions and large-scale outdoor displays. The technology has also led to the development of OLED (Organic Light Emitting Diode) displays, which further enhance image quality by using organic compounds to emit light. OLED displays are known for their exceptional color accuracy and viewing angles, as well as their ability to produce true blacks, which contributes to a more immersive viewing experience.
Advantages of LED Displays
LED displays offer several advantages over traditional LCDs, including:
- Higher Brightness: LED displays can achieve higher brightness levels, making them suitable for use in well-lit environments.
- Better Energy Efficiency: LED technology is generally more energy-efficient than traditional LCD backlighting, leading to lower power consumption.
- Longer Lifespan: LED displays tend to have a longer operational lifespan compared to other display technologies, reducing the need for frequent replacements.
In addition to these advantages, LED displays are also more versatile in terms of form factor and design. They can be manufactured in various shapes and sizes, allowing for creative applications in advertising, architecture, and art installations. For instance, flexible LED displays can be bent or curved to fit unique spaces, while large-scale LED walls can create stunning visual experiences for concerts and events. Furthermore, advancements in LED technology have led to the introduction of microLED displays, which promise even higher resolutions and pixel densities, paving the way for future innovations in the display industry.
Comparing LCD and LED Displays
When choosing between LCD and LED displays, it’s essential to understand the differences and how they may impact the user experience. While both technologies have their advantages, they cater to different needs and preferences.
Image Quality
In terms of image quality, LED displays generally outperform traditional LCDs. The ability to control individual pixels allows for greater contrast and more vibrant colors. However, advancements in LCD technology, such as LED backlighting, have improved the performance of LCD screens significantly, narrowing the gap between the two.
Cost Considerations
Cost is a significant factor when choosing a display technology. Traditional LCDs are often more affordable than LED displays, making them a popular choice for budget-conscious consumers. However, as LED technology becomes more widespread, the price difference is gradually decreasing.
Future Trends in Display Technology
The display technology landscape is continually evolving, with innovations driving improvements in performance, efficiency, and user experience. As technology advances, several trends are emerging that are likely to shape the future of displays.
MicroLED Technology
MicroLED technology is an exciting development that promises to combine the best features of LCD and LED displays. MicroLEDs are tiny, self-emissive diodes that can produce high-quality images with exceptional brightness and contrast. This technology has the potential to create ultra-thin displays with improved energy efficiency and longevity.
Flexible Displays
Flexible display technology is also gaining traction, allowing screens to bend and curve without compromising image quality. This innovation opens up new possibilities for device design, enabling manufacturers to create more versatile and portable devices.
Conclusion
In summary, LCD, touch screen, and LED display technologies each play a vital role in the modern digital landscape. Understanding the differences and applications of these technologies can help consumers make informed decisions when selecting devices. As advancements continue to shape the future of display technology, users can expect even more innovative solutions that enhance their interaction with the digital world.
Whether it’s the clarity of an LCD screen, the interactivity of touch technology, or the brilliance of an LED display, each technology contributes uniquely to the way we experience visual content. Keeping abreast of these developments ensures that users can choose the best options to meet their needs, whether for personal use or professional applications.
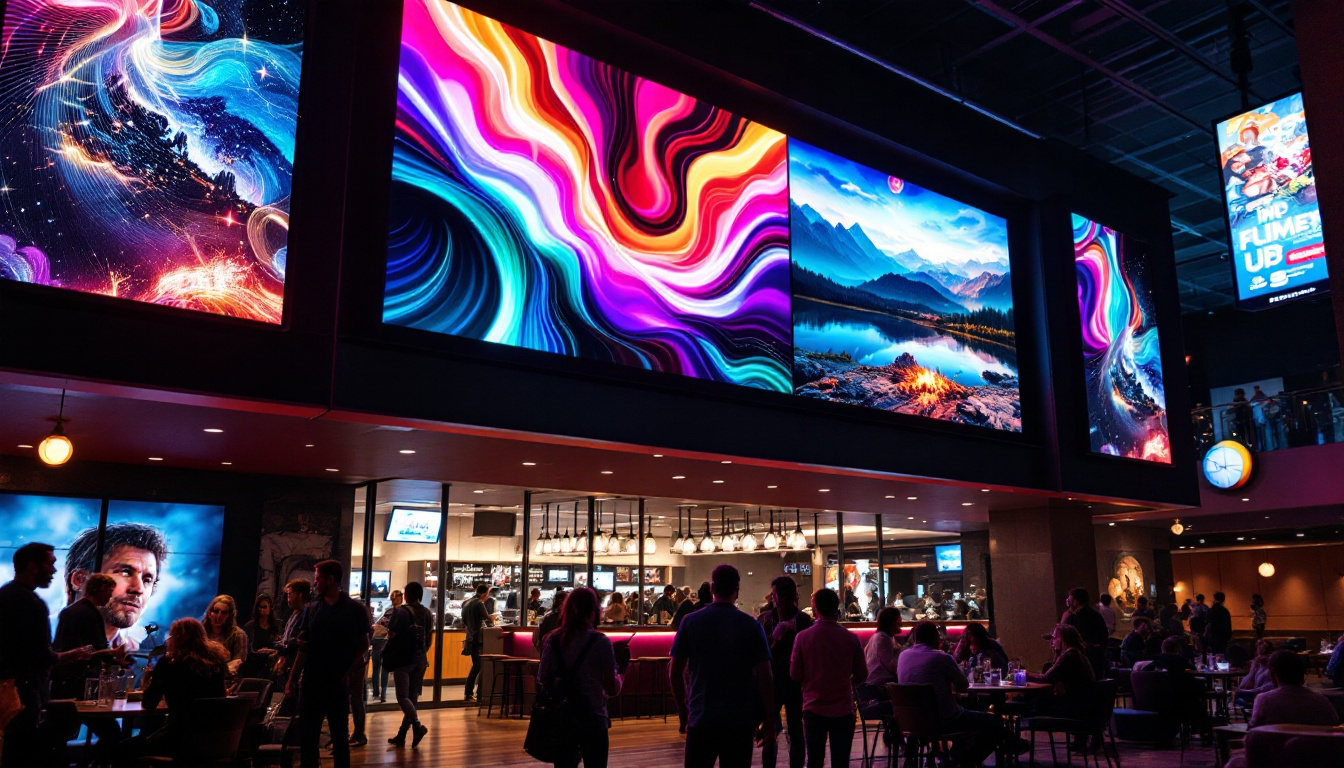
Discover LumenMatrix’s Innovative LED Displays
As you consider the future of display technology for your personal or professional needs, LumenMatrix stands at the forefront of LED innovation. With a wide array of solutions ranging from Indoor and Outdoor LED Wall Displays to specialized options like Vehicle, Sports, and Floor LED Displays, LumenMatrix is committed to transforming your visual communication. Experience the difference with our Custom, All-in-One, and Transparent LED Displays designed to captivate and engage your audience. Check out LumenMatrix LED Display Solutions today and step into a world of vivid imagery and dynamic storytelling.